how do we bootstrap from trust we already have, to the trust we want to have to thrive (and need to have for problems we care about)?
[This post written in about 15 minutes, as part of my new experiment in Writing It Live!]For a much much longer take on the same question, with more examples and angles, read my mini ebook How we get there: a manual for bootstrapping meta-trust.

If you like one-pager bullet-list style posts, I have more:
Sixth post in “I can tell for myself” sequence. On the last episode… Reality distortion: “I can tell, but you can’t”, which opened up our exploration of interactions between one person who is in touch with their own direct-knowing and another person who is more just taking others’ word for it. With this post we’re finally reaching some of the core ideas that the other posts have been a foundation for.
(I left “guru” in the title of this part, because “guru dynamics” are what I call this phenomenon, but I decided not to use the word “guru” in the body of the text. It’s a loanword that originally means “teacher” but of course in English has the connotations associated both with spiritual teaching in particular and thus also with the dynamics I want to talk about here, some of which are well-documented in The Guru Papers. To be clear, I don’t think guru’ing, as a role, is necessarily bad—it’s just extraordinarily hard to do well. But “guru” as a frame… the roles are probably best not thought of as a student-teacher relationship at all. Instead, perhaps, “one who’s remembering” and “one who’s reminding”: ancient wisdom tradition words for this like “sati”, and “aletheia” mean “remembering” or “unforgetting”. Those are awkward though.)
Things get weird when a person who has consistent access to their sense of “I can tell for myself” across many domains—especially spiritual, interpersonal, esoteric, subtle, ineffable., ones—finds their way into a position where they’re trying to help others develop this capacity for themselves.
This happens remarkably often! There are many factors that contribute to this, of which here are six:
So it’s very common for someone who has developed their sense of self-authored direct-knowing to find themselves surrounded by a bunch of people who also want to develop this capacity. (We’ll explore in a later post why there’s often precisely one teacher per learning context; the previous post also hints at it.)
But attempting to teach “I can tell for myself” (or self-trust, or whatever you call it) leads to what is nearly a paradox:
Suppose that when someone says something you don’t understand or resonate with, your two available moves are either to (1) reject what they’re saying or (2) “take their word for it”—a condition which is tautologically the starting point for someone who has learned to not trust themselves in the face of what someone else is saying, and is wanting to develop that self-trust—then if I’m trying to convey “how to tell for yourself”, you’ll either… reject what I’m saying as senseless, or… take my word for it that this is in fact how to tell for yourself and you just need to do it exactly as I say yessirree!
…which is not “I can tell for myself”. Or is it?
» read the rest of this entry »A tangent off the “I can tell for myself” sequence, between post 4 & 5.
There’s a thing it feels like to know 5+5=10.
Wait—that’s exactly the opposite of what I mean. There are many things in feels like—in some sense at least one per person who’s ever known it, in another sense as many as times it’s been known! And while I can know 5+5=10 is so true that I can be certain that if you know what I mean by 5 and + and = and 10, that you’ll agree… my knowing and your knowing are still different.
Concretely, I might be knowing 5+5=10 from a verbal memorized table that never did me wrong, and you might be imagining two nickels and a dime. Or one of us has an experience of beholding 10 fingers, 5 on each hand, the other has a sense of 5 having a halfness to it, in relation to 10, related to thinking in decimals for a lifetime. But those are just four abstract descriptions, under which many yet-unique experiences of knowing 5+5=10 could be binned—and many could not. And either or both of us might go about knowing 4+8=12 very differently than we know 5+5=10.
And those knowings are likely yet different from what it would feel like to know such a thing together.
This applies to all knowings: mundane and spiritual, mathematical and episodical. My knowing is not your knowing, and neither one is our knowing. And they aren’t the thing that is known.
Something can be true without being known: I could write a computer program that would generate a true statement that nobody had ever seen or known (such as 12364871317234+1=12364871317235, but imagine it’s longer and more convoluted) and it would still be true within that formal system, but it wouldn’t be known unless or until someone went and knew it. It could be true that there’s life on a particular exoplanet 51 Pegasi b, but it’s not currently known (as far as I know—if I’m mistaken, pick a different exoplanet). There are philosophical questions about who counts as “someone” and I am mostly going to say “definitely at least humans, in some cases animals or parts-of-humans”.
In the previous paragraph I was talking about things that are true but not known by anyone. There are also true things that are known by someone but not by someone else. You can even know OF a “true fact”, without actually knowing it. Here’s one: I’m typing this paragraph while listening to Tycho’s album Dive. One of my favorite albums. You could memorize this fact and perhaps pass it onto many other people… and maybe you even have good reason to believe me, because I’m a pretty honest guy in general and have no incentive to lie or whatever, but you don’t know it. Not directly. You can’t tell for yourself, but you can take my word for it.
A kid can know that “Santa comes on Christmas eve!” The question of whether Santa is “real” in the same senses in which the kid’s parents are real is not vital to the kid’s knowing—the kid knows that there are presents from Santa, and various other evidences such as cookie crumbs or in the case of very theatrical parents, sooty bootprints or whatever… insofar as the phrase “Santa comes on Christmas eve!” refers to that event, the kid can tell for themself that that happens. Santa sure doesn’t come on a randomly selected Tuesday in late April, for the purpose of leaving broken toasters on the lawn!
» read the rest of this entry »“I can tell for myself” is the kind of knowing that nobody can take away from you.
Nobody can take it from you, but they can get you to hide it from yourself. They can put pressure on you to cover up your own knowings—pressure that’s particularly hard to withstand when you’re relatively powerless, as a kid is. This pressure can come from the threat of force or punishment, or simply the pain of not being able to have a shared experience of reality with caregivers if you know what you know and they don’t allow such a knowing.
Ideally, we integrate others’ word with our own sense of things, and smoothly navigate between using the two in a way that serves us and them. Others would point out where they can see that we’re confused about our own knowings, and we’d reorient, look again, and come to a new sense of things that’s integrated with everything else.
But, if you’re reading this, you were probably raised in a culture that, as part of its very way of organizing civilization over the past millennia, relied on getting you to take others’ word for it even when you could tell that something about what they you being told was off… to the point that you probably learned that your own knowing was suspect or invalid, at least in some domains.
Did you cover up your natural sense of appetite, with politeness, when parents or grandparents said “You haven’t eaten enough! You have to finish what’s on your plate.”? Did you cover up your natural sense of thirst when parents or teachers said “No, you don’t need a drink right now.”? Did you forget how to listen to the building pressure in your lower abdomen, in the face of a “You don’t have to pee! You just went!”?
Did you override your sense of relevance and honesty when someone said “You can’t say that!”? Maybe someone close to you said “You didn’t see that!” or “you didn’t hear that!” or “that didn’t happen!” — as a command, not a joke… did that make it harder to listen to your own senses or vision or hearing? Not altogether, but in situations where you could tell others wouldn’t like you to know what you know. Did someone say “Come on, you know I would never lie to you,” twisting your own sense of trust in others’ honesty and dishonesty, around the reality that you did not, in fact, know that, and (since this was coming up at all) may have been doubting it?

File this one under Evolution of Consciousness studies.
I’ve been working on a new theory inspired by Andrew Cutler’s Snake Cult of Consciousness article and Eve Theory of Consciousness articles, about the evolving relationship between what you could call id, ego, and superego. I’m honestly not particularly stoked about those terms, for lots of reasons, but they do seem to roughly map onto the thing that I’m looking at, so here we go.
This post also relates to some other thinking I’ve been doing over the last few years about how egos are necessary for managing your attention & care in relation to external systems that might co-opt your attention & care if you’re too open.
Here’s part of the post in a tweet:
Andrew writes:
In Freudian terms, we had an animal id for millions of years. We then evolved a super-ego, the simulated view of society in our head. Implicitly, there was a node resolving conflicts between these competing interests: a subconscious ego. A fateful encounter with snake venom allowed someone to perceive this process and she could not unsee it. Henceforth, she perceived and identified with her ego, the agent tasked with navigating the tribe’s moral code. Or in the parlance of the time, she “became as the gods, knowing good and evil.”
That is, the Fall, from a nondual mode to one dualistically separated from an experience of flow with god-ness. Ouch. The transition from the first memetic operating system to the second.
What are we talking about with id, ego, and superego. First thing to know is that those terms made a lot more sense before they were translated from German into Latin. In Freud’s original work, they were “Es, Ich, & Über-Ich”—the it, the I, and the over-I. Now admittedly “I” is a bit unwieldy, visually and acoustically, but the translation to latin made these notions seem very weird and foreign and reified, rather than natural parts of our experience.
At any rate! It is also helpful to have these other words for them for various reasons now. Here’s my take:
The rest of this post will be exploring some of the implications of this model for the evolution of consciousness, as I see it. I’m sure I’ll see more within a few months, so I wanted to share these now while they’re fresh.
The genesis of this post came while I was visiting an old dear friend in another city and staying at an airbnb a short walk from his place. We were talking about the Snake Cult model and some related ones, and as the night got on we started talking about whether he might go home briefly, in part to pick some stuff up and in part to see his partner. And we were kind of feeling into what made sense, and then we noticed that there was a tension in him between a sense of wanting to be a good husband (by connecting with his partner, tucking them in, and helping them de-stress before bed, especially given that their work is stressful at the moment) and wanting to be a good friend (by continuing to hang out with me, uninterrupted).
» read the rest of this entry »Or more straightforwardly:
“how to give feedback to somebody about something that you’re noticing going on for them, where you suspect that if you try to acknowledge it they’ll get defensive/evasive & deny it”
One of the core principles of my Non-Naive Trust Dance framework is that it’s impossible to codify loving communication—that any attempt to do so, taken too seriously, will end up getting weaponized.
Having said that, maybe if we don’t take ourselves too seriously, it would be helpful to have a template for a particularly difficult kind of conversation: broaching the subject about something you’re noticing, where you expect that by default what will happen is that you won’t even be able to get acknowledgement that the something exists. This can be crazy-making. I often call it “blindspot feedback” although for most people that phrase carries connotations that usually make people extra defensive rather than more able to orient and listen carefully.
To see more about how I think about this, you can read this twitter thread:
But I want the template to stand alone, so I’m not going to give much more preamble before offering it to you. The intent is that this template will help people bridge that very first tricky step of even managing to acknowledge that one person is seeing something that the other person might not be seeing, and having that be okay.
I’m calling this alpha-testing not beta-testing because while I know the principles underlying this template are sound, and I’ve tested the moves in my own tough conversations and while facilitating for others… as of this initial publication the template itself has been used zero times, so I don’t want to pretend that it itself is well-honed.
So I’d like to collect lots of perspectives, of what people think of the template just from looking at it, and of how conversations go when you try to use the template for them.
Without further ado, here’s a link to the template.
I’d love if you gave me your thoughts while you read it. To do that, make a copy, name it “Yourname’s copy of Template” then highlight sections and leave comments on them, then give comment access to me (use my gmail if you have it, or malcolm @ this domain). That would be very helpful. Even just little things like “ohhhh, cool” or “I don’t get why you’d say this” or “would it work to rephrase this like X, or would that be missing something important?”
To try it out, make a copy, then fill it out, and do what you want with it. Then, if you’d like to help me iterate on it or would otherwise like your experience of using it seen by me, fill out this form and let me know how it worked for you (or didn’t).
I wrote this addressed to a learning community of a few dozen people, based in Ontario, that evolved from the scene I used to be part of there before I left in late 2020. I’m about to visit for the first time in nearly 2 years, and I wanted to articulate how I’m understanding the purpose & nature of my visit. It’s also aimed to be a more general articulation of the kind of work I’m aiming to do over the coming years.
This writing is probably the densest, most complete distillation of my understandings that I’ve produced—so far! Each paragraph could easily be its own blog post, and some already are. My editing process also pruned 1700 words worth of tangents that were juicy but non-central to the point I’m seeking to make here, and there are many other tangents I didn’t even start down this week while writing this. Every answer births many new questions. See also How we get there, which begins with the same few paragraphs, then diverges into being a manual for doing this process.
To “jam” is to improvise without extensive preparation or predefined arrangements.
“Convening” means coming together, and Ontario is of course that region near the Great Lakes.
As for the “meta-protocol”…
It seems to me that: consistent domain-general group flow is possible and achievable in our lifetimes. Such flow is ecstatic and also brilliant & wise. Getting to domain-general group flow momentarily is surprisingly straightforward given the right context-setting, but it seems to me that it usually involves a bit of compartmentalization and is thus unsustainable. It can be a beautiful and inspiring taste though. (By “domain-general” I mean group flow that isn’t just oriented towards a single goal (such as what a sports team has) but rather an experience of flow amongst the group members no matter what aspects of their lives or the world they turn their attention to.)
It seems to me that: profound non-naive trust is required for consistent domain-general group flow. This is partially self-trust and partially interpersonal trust.
It seems to me that: in order to achieve profound non-naive trust, people need to reconcile all relevant experiences of betrayal or interpersonal fuckery they’ve had in their life. This is a kind of relational due diligence, and it’s not optional. It’s literally the thing that non-naive trust is made out of. That is, in order for a group to trust each other deeply, they need to know that the members of that group aren’t going to betray each other in ways they’ve seen people betray each other before (or been betrayed before). Much of this is just on the level of trusting that we can interact with people without losing touch with what we know. So we either need to find a way to trust that the person in front of us won’t do something that has disturbed us before, or that we ourselves aren’t vulnerable to it like we were before, which involves building self-trust. It takes more than just time & experience to build trust—people need to feel on an embodied level why things go the way they’ve gone, and see a viable way for them to go differently.
It seems to me that: people attempt to do this naturally, whenever they’re relating, but understanding what’s going on and how to make it go smoothly can dramatically increase the chances of building trust rather than recapitulating dysfunctional dynamics by trying to escape them.
» read the rest of this entry »In which I answer 6 questions from a friend about my Non-Naive Trust Dance framework. I’ve said a lot of this before, but kind of all over the place, so here it is collected together, as yet another starting point.
The questions:
My experience of writing this post has caused me to have a sort of meta-level answer to a question I see behind all of these questions, which is “why is the NNTD so important? should I care?” And my answer is that I don’t actually think NNTD is that significant on its own, and that most people should care if it intrigues them and seems useful and not otherwise. What makes the NNTD important is that it’s a new & necessary puzzle piece for doing world-class trust-building, which is necessary for making progress on collective consciousness, and that is important. But if you’re not working on that, and NNTD doesn’t interest you, then maybe you want to put your attention elsewhere!
It is, perhaps unfortunately, all 3 of those things. I would say that in some sense it’s mostly a worldview or a theory, and any practice that emerges out of that could ultimately be described as simply being what it is. Certain practices make more or less sense in light of the theory, but it’s descriptive rather than prescriptive.
So as a worldview, the NNTD view sees all beings as constantly engaged in trust-dancing. “Trust” and “truth” have the same root, and trust can be thought of as essentially subjective truth, so trust-dancing with reality is figuring out what seems true from your vantage point. Where naivety comes in is that humans have a tendency to try to interfere with each others’ sense of what’s true, resulting in apparent trust that’s actually layered on top of repressed distrust.
» read the rest of this entry »I scheduled this post to go live as a showtime, then realized I wasn’t sure if “consciousness” is the right way to even frame this, but I let it go live anyway. In some sense it could be called “sanity”, but that has its own challenging connotations. I use both terms sort of synonymously below; I might decide later that yet a third word is better. There’s also a lot more that I can—and will—say about this!
I figure collective consciousness can be summarized as the capacity for a group of people to:
(Jordan Hall’s 3 facets of sovereignty: perception, sensemaking and agency.)
I like to say “Utopia is when everyone just does what they feel like doing, and the situation is such that that everyone doing what they feel like doing results in everyone’s needs getting met.” On a smaller group, a sane We is when everyone in the We does what they feel like in the context of the We, and they are sufficiently coherently attuned to each other and the whole such that each member’s needs/careabouts get met.
In some sense, obviously, if there existed an X such that if you supported the X it would cause everything you want to be achieved better than you could manage on your own, you’d want to support the X. Obviously, from the X’s perspective, it would want to support the individuals’ wants/needs/etc to get met so that they have more capacity to continue supporting it supporting them supporting it [ad infinitum]. This is the upward spiral, and it’s made out of attending to how to create win-wins on whatever scale.
As far as I can tell, there can’t exist such an X that is fully outside the individual(s) it is supporting. In order for it to actually satisfy what you actually care about, consistently and ongoingly, it needs a direct feedback loop into what you care about, which may not be what you can specify in advance. Thus you need to be part of it. The system gives you what you need/want, not what you think you need/want, in the same way that you do this for yourself when you’re on top of things. Like if you eat something and it doesn’t satisfy you, you get something else, because you can tell. (This is related to goodhart and to the AI alignment puzzle).
Fortunately, as far as I can tell, we can learn to form We systems that are capable of meeting this challenge. They are composed of ourselves as individuals, paying attention to ourselves, each other and the whole in particular ways. Such a We can exist in an ongoing long-term explicit committed way (eg a marriage) or one-off task-based unremarkable ad hoc way (eg a group gathers to get someone’s car unstuck, then disappears). Or it could be a planned and explicit temporarily-committed group (eg a road trip) or an emergent spontaneous group (eg some people who meet at burning man and end up being adventure buddies for the rest of the day, taking care of what arises).
While queuing up the 100× vision post last week, I realized I hadn’t published another vision doc that I wrote awhile back and had been sharing with people, so I figured out would be good to get that out too. In contrast to the 100× vision, which is imagining the 2030s, this one is the adjacent-possible version of the vision—the one where if you squint at the current reality from the right angle, it’s already happening. I wrote this one originally in November 2020. There’s also A Collaborative Self-Energizing Meta-Team Vision, which is a looser sketch.
This is intended to evoke one possibility, not to fully capture what seems possible or likely.
In fact, it is highly likely that what happens will be different from what’s below.
Relatedly, and also central to this whole thing: if you notice while reading this that you feel attracted towards parts of it and averse to other elements (even if you can’t name quite what) then awesome!
Welcome that.
Integrating everyone’s aversion or dislike or distrust or whatever is vital to steering towards the actual, non-goodharted vision. And of course your aversion might be such that it doesn’t make sense for you to participate in this (or not at this phase, or not my version of it). My aim is full fractal buy-in, without compromise.
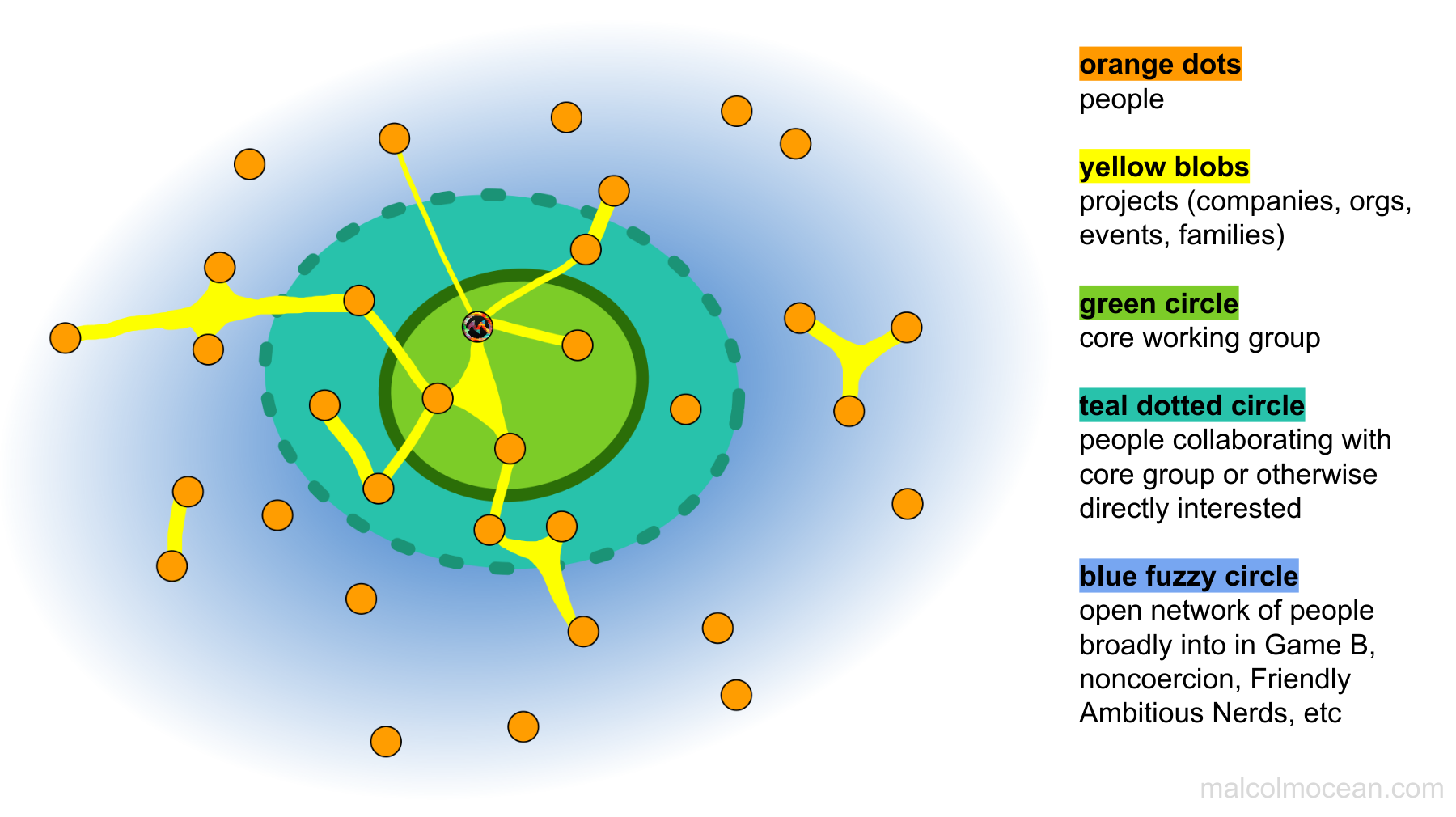
This diagram (except for the part where one of the people is marked as me 😉) could apply to any network of people working on projects together, that exists around a closed membrane, but I want to elaborate a bit more specifically about what I have in mind.
The Collaborative self-energizing meta-team vision public articulation 2020-10-19 is describing the outermost regions of the above diagram, without any reference to the existence of the membranes. The open-network-ness is captured by this tweet:
This is a beacon—want to work with people doing whatever most deeply energizes you? Join us!…how? There’s no formal thing.
Joining = participating in this attitude.
The attitude is one of collaboration in the sense of working together, and in particular working together in ways that everybody involved is excited about and finds energizing and life-giving. Where people are motivated both by the work they’re doing as part of the collaboration, and by the overall vision. That’s not to say it’ll all be easy or pleasant or straightforward—working with people is challenging! And that’s where the other layers come in.
I’m now going to jump to the innermost, closed membrane, because the dotted-line teal group kind of exists as a natural liminal area between that and the wider group.
» read the rest of this entry »